Font Family Cursive Not Working? Here’s How to Make it Work:
Font Family Cursive is not working? You’ve probably already tried renaming it and using a different name. If that’s the case, you probably want to exclude it from your project. If that’s not possible, here are some ways to make it work.
This article describes the font-family property and how to use it correctly. You can also learn about how to make fonts thicker by using them as headings.
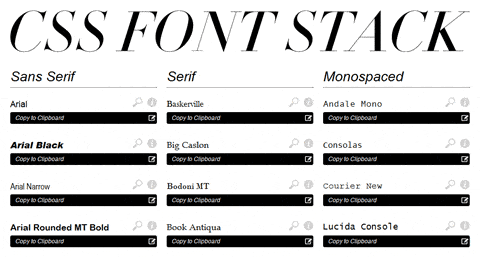
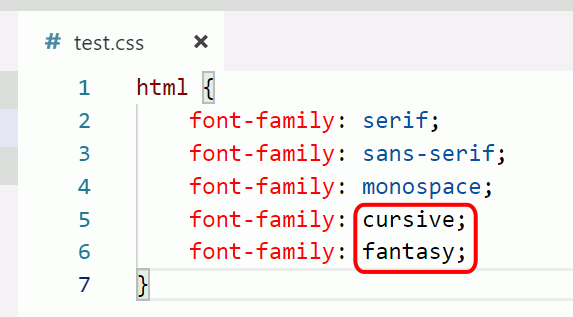
Font-family property specifies a list of fonts:
The font-family property specifies a set of fonts for an element. It can hold several names and acts as a fallback system for other font-related properties. A font family is a group of fonts with similar styles and designs, typically designed by a typographer. Each font within a family differs in slant, weight, and other characteristics. If your element uses several fonts, you can list them one at a time in the font-family property.
Usage of Font Family:
To use the font-family property, you must include a “family” attribute. The name of the font should contain whitespace, and font size should be expressed in absolute units like px. The font-family property is most useful for personal use. You can use font size for titles and subtitles, and the font-family property specifies the size of those elements. So you must quote a font name when specifying a family.
Also, you can also use the font-family property to specify a list of custom fonts. This way, you can link a custom font file to a web page. Then, you can include a list of custom fonts as well as a list of generic fonts. When using a custom font, you need to include it in quotation marks, which will ensure that it is used correctly.
Font size specifies the style of a font:
The font size is a CSS property that determines how large or small a text element is. It is the size that the font appears in the browser. There are two different types of font size, absolute and relative. The latter is more flexible and compatible with older browsers. The former is more flexible but less compatible with older browsers. The font size can be expressed in absolute or relative terms, depending on the use of the font.
Features of Font Family:
The font-size property sets the height and width of the font. It is the most common font size setting and affects the size of the text. The font-size property accepts percentages and keywords to specify the size. The font-size property is a required property when declared in the font shorthand, but can’t be negative. However, it may still be necessary to use relative values if you want to customize the font size on your website.
When specifying the size of a font, it’s best to use the relative unit of measure. While points and pixels are both accurate, they render differently across platforms. Browsers cannot resize fonts that are rendered in absolute units. Fortunately, there are other ways to specify the font size. You can use relative units, like ems and percentages. Common 12-point font size is equivalent to a single em.
Fonts look thicker when used in a heading:
Most cursive fonts look thin when used in a heading, but they can create a unique effect. For example, the Italiano script font has tails that connect to the next letter. This type of font would be perfect for a restaurant menu heading. It is also considered a fancy font. As a result, cursive fonts are often difficult to read on small text, such as a heading.